Effective risk control measures are systematic approaches to eliminate or minimize workplace hazards. This guide outlines proven methodologies aligned with ISO 45001, OSHA, and hierarchy of controls principles to help organizations implement robust safety protocols.
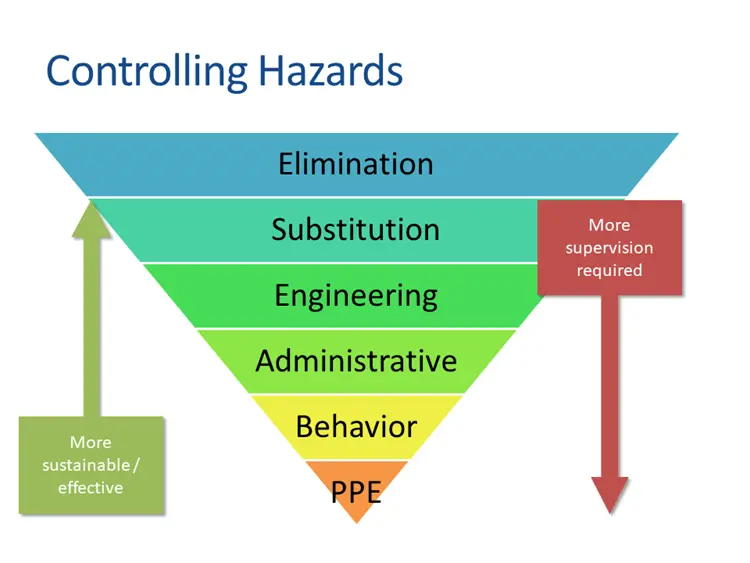
Hierarchy of Controls
(Most to Least Effective)
| Control Level | Measure | Example | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Elimination | Remove hazard | Replace toxic chemical with non-toxic alternative | 100% risk removal |
| 2. Substitution | Replace hazard | Use water-based paints instead of solvent-based | Up to 90% reduction |
| 3. Engineering Controls | Isolate people | Machine guards, ventilation systems | 70-85% reduction |
| 4. Administrative Controls | Change work practices | Job rotation, training programs | 50-70% reduction |
| 5. PPE | Protect worker | Hard hats, respirators | <50% reduction |
1. Construction
-
Fall Prevention: Guardrails > Safety nets > Harnesses
-
Struck-By Hazards: Exclusion zones > Spotter systems
2. Manufacturing
-
Machine Safety: Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) > Light curtains
-
Chemical Exposure: Closed systems > Local exhaust ventilation
3. Healthcare
-
Biohazards: Needleless systems > Sharps containers
-
Ergonomics: Lift assists > Patient transfer training
4. Oil & Gas
-
H2S Protection: Fixed detectors > Escape respirators
-
Fire Prevention: Inert gas systems > Hot work permits
What Will You Learn?
- Implementation Framework
- Hazard Identification
- JSA (Job Safety Analysis)
- HAZOP Studies
- Risk Assessment
- Probability/Severity Matrix
- Bowtie Analysis
- Control Selection
- ALARP Principle (As Low As Reasonably Practicable)
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Monitoring & Review
- Safety audits
- Near-miss reporting systems
Student Ratings & Reviews

No Review Yet

No Data Available in this Section


